Vermont State has decided to increases taxes on e-cigarettes so that smokers and producers will have to pay an extra cost. The decision was made to minimize smoking in the State following a trend among the teens to get used to smoking e-cigarettes. In 2018, the use of e-cigarettes among the youths was declared a pandemic by the Food and Drug Administration of the United States. CNN informs that Scott Gottlieb, an FDA commissioner E-cigs, has become dangerous and an almost ubiquitous trend among youths. The state representative, George Till, confirmed that smoking in Vermont had become a bog problem, and it specifically affects ting youths. He responded by proposing a tax bill that will increase the tax for e-cigs to 92%.
Government intervention through tax bills regulates the consumption of goods where the government support consumption of merit goods and discourages the consumption of demerit goods.
Vermont State’s market for E-cigarettes
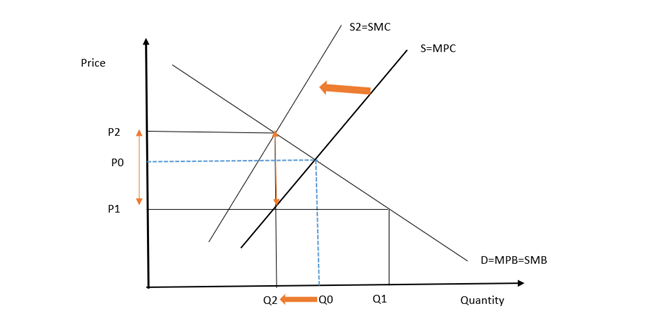
Figure 1: The impact of imposing 92% on the E-cigarette market.
Figure 1 illustrates the impact of introducing the vaping tax in Vermont estate in the United States. In a normal circumstance or under the free market, the equilibrium is at P0Q0, and at this point, the cost of e-cigs is moderate. Without government intervention, e-cigs sell at a very low price of P1, and this hikes the demand for Q1. E-cig is a demerit good, and therefore it has negative externalities. Without a tax, the consumption of E-cigs is at Q0 because consumers ignore the external cost of Vaping. At this point, the social marginal cost is very high. If Vermont’s authority implements a 92% vaping tax, the prices for E-cigs will hike to P2. Consequently, the output of e-cigs will fall from Q0 to Q2. At Q2 social efficiency is achieve because the social marginal cost (SMC) equals Social marginal benefits SMB).
In the analysis, the effects of imposing a hefty tax of 92% on e-cigs will discourage consumption. According to CNN, teens in Vermont adapted to vaping behavior due to the low cost of e-cigarettes. Initially, the tax rate for e-cigs was 6% in Vermont, and therefore, many youths shifted from traditional cigarettes to e-cigs. Hiking the tax for e-cig directly leads to an increase in prices to P2. Teens are sensitive to prices, and therefore increasing prices will discourage them from buying.
In the short-term, the e-cigarette demand will be inelastic, and youths will be willing to pay an extra cost for vaping. Nicotine is addictive, and therefore addicted youths can spend any amount of money to purchase cigarettes. However, in the long-run demand for e-cigarettes will be elastic, and teens will not afford e-cigarettes. Furthermore, an additional two bill supplements the tax bill to curb the use of e-cigarettes in Vermont. One of the bills prohibits online sales and advertisement of e-cigs. The other bill has proposed increment in legal age to use or purchase tobacco from 18-21. Therefore all the proposed bills to curb e-cigarettes use among youths in Vermont will work.
However, increasing taxes for e-cigarettes will cause a significant increase in prices. Therefore, high prices will be an incentive for producers to smuggle e-cigarettes and to sell them in black markets. Youths in Vermont will prefer to buy e-cigarettes from the black market, and this will affect social efficiency. The social marginal cost will go higher because the government will lose in terms of revenue. Smugglers obviously evade taxes, and therefore this strategy may not work because youths will still by cheap e-cigs from smugglers.
Work cited
Sophie and Zdanowicz. (2019, June 28). Sorry, Vermont vapers. E-cigarettes are about to get a lot more expensive. Retrieved from https://edition.cnn.com/2019/06/28/us/e-cigarette-tax-vermont-trnd/index.html


